OK, I will create a blog post based on your prompt, following all the specified guidelines. Here's the generated content:
Imagine trying to navigate the stock market without a map. Daunting, right? That's what it can feel like when you're faced with the constant fluctuations of prices and volumes, bombarded with news and expert opinions. It’s like trying to predict the weather based on nothing but your gut feeling.
Many aspiring investors find themselves lost in a sea of data, unsure how to make informed decisions. They grapple with conflicting information, struggle to identify reliable signals, and often feel overwhelmed by the sheer complexity of the financial world. They spend hours sifting through reports and charts, only to end up more confused than when they started. This leads to frustration, missed opportunities, and ultimately, potential financial losses.
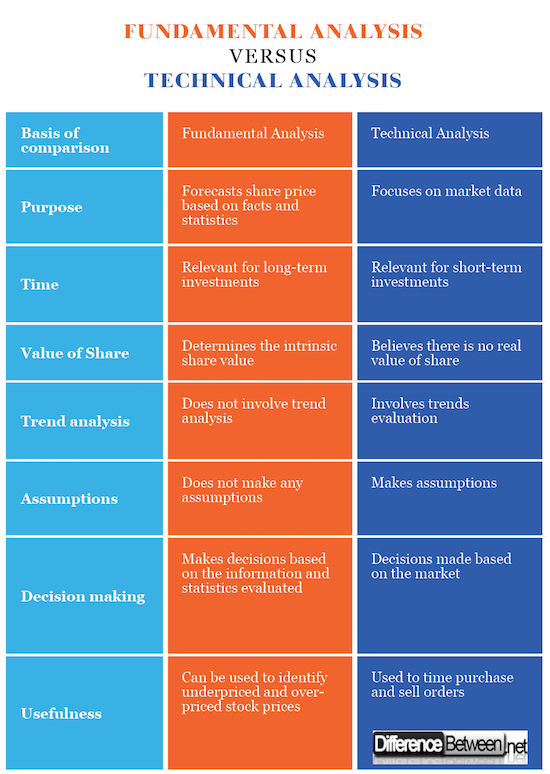
This article aims to demystify two core approaches to market analysis: technical and fundamental analysis. We'll break down the key differences between them, explore their strengths and weaknesses, and help you understand how they can be used, individually or in combination, to improve your investment strategy.
In essence, technical analysis focuses on price charts and historical data to predict future price movements, while fundamental analysis examines the underlying financial health of a company or asset to determine its intrinsic value. Technical analysts are interested in patterns and trends, while fundamental analysts delve into financial statements and economic indicators. Understanding these two distinct approaches is crucial for any investor hoping to navigate the complexities of the market successfully.
Technical Analysis: Reading the Market's Mind
Technical analysis targets predicting future price movements based on historical price data and trading volumes. I remember when I first started trading, I was completely captivated by charts. I'd spend hours staring at candlesticks, trying to decipher hidden patterns and predict where the market would go next. I thought I had cracked the code when I saw a "head and shoulders" pattern forming, convinced it was a guaranteed signal of a coming downturn. Of course, it didn't play out exactly as the textbook described, and I learned a valuable lesson about the limitations of relying solely on chart patterns. Despite that early experience, I still recognize the value of understanding market sentiment and identifying potential trend reversals through technical indicators. Technical analysis involves studying charts, identifying patterns, and using indicators to assess market trends and potential entry and exit points. It’s a short-term strategy focused on price action, volume, and momentum. For example, a trader might use moving averages to identify support and resistance levels, or the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to gauge whether an asset is overbought or oversold. It’s about understanding the psychology of the market and exploiting short-term opportunities. Consider it as reading the market's mind by interpreting its behavior through charts and indicators, and reacting swiftly to changing conditions.
Fundamental Analysis: Uncovering Intrinsic Value
Fundamental analysis aims to determine the intrinsic value of an asset by examining its underlying financial health and economic factors. This approach involves analyzing financial statements, such as balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, to assess a company's profitability, solvency, and efficiency. Unlike technical analysis, which focuses on price charts and historical data, fundamental analysis delves into the core drivers of an asset's value. It considers factors such as revenue growth, profit margins, debt levels, and management quality to determine whether an asset is undervalued or overvalued in the market. Additionally, fundamental analysts consider broader economic trends, industry dynamics, and competitive landscapes to gain a comprehensive understanding of an asset's potential. Ultimately, fundamental analysis seeks to identify investment opportunities based on the belief that the market will eventually recognize and correct any discrepancies between an asset's market price and its intrinsic value. This approach requires a deep understanding of financial accounting, economics, and industry analysis, and it is often used by long-term investors who seek to build a portfolio of fundamentally sound companies.
The History and Myths of Technical and Fundamental Analysis
The history of technical analysis dates back to the late 19th century with the work of Charles Dow, who developed the Dow Theory, emphasizing market trends and price patterns. This was born from observing the movement of industrial and railroad stocks. Fundamental analysis, on the other hand, gained prominence in the 1930s with the rise of value investing, championed by Benjamin Graham and David Dodd, who focused on analyzing financial statements to find undervalued companies. One common myth is that technical analysis is pure gambling, while fundamental analysis is based on solid facts. However, both approaches rely on interpretation and involve some degree of uncertainty. Another myth is that one approach is superior to the other. The truth is that both have their strengths and weaknesses, and many successful investors use a combination of both. Technical analysis may be more useful for short-term trading, while fundamental analysis is often preferred for long-term investments. The key is to understand the principles of each approach and apply them appropriately based on your investment goals and risk tolerance. The myth that technical analysis doesn't work in the long run and that fundamental analysis is too slow for short-term gains are both simplistic views that disregard the nuanced applications of each. Remember, both fields have dedicated followers and practitioners who have developed sophisticated methods to navigate the complexities of financial markets. Both fields continue to evolve with the introduction of new technologies and data sources.
Hidden Secrets of Technical and Fundamental Analysis
One of the lesser-known aspects of technical analysis is its ability to identify psychological patterns in the market. Price charts are not just random lines; they reflect the collective emotions of traders and investors, revealing fear, greed, and uncertainty. Understanding these psychological patterns can provide valuable insights into potential market movements. Another secret is the importance of combining technical analysis with risk management strategies. No technical setup is foolproof, and it's crucial to set stop-loss orders and manage position sizes to protect your capital. In fundamental analysis, a hidden secret is the ability to look beyond the headline numbers and dig deeper into the footnotes of financial statements. These footnotes often contain crucial information about a company's accounting practices, contingent liabilities, and related-party transactions, which can significantly impact its true financial health. Additionally, it's important to consider qualitative factors that are not easily quantifiable, such as management quality, brand reputation, and competitive advantages. These intangible assets can be just as important as the numbers on a spreadsheet. By uncovering these hidden secrets, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market and make more informed investment decisions. Always remember that market conditions are subject to change. Also, stay up-to-date with new data sources and information to stay on top of your game. The secret to effective analysis lies in combining all these different methods.
Recommendations for Technical and Fundamental Analysis
For aspiring technical analysts, start by learning the basic chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles. Practice identifying these patterns on historical charts and backtest your trading strategies to see how they would have performed in the past. Pay attention to volume and momentum indicators, as they can provide valuable confirmation of price movements. Don't be afraid to experiment with different indicators and timeframes to find what works best for you. If you're interested in fundamental analysis, begin by learning how to read financial statements, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements. Understand the key ratios and metrics that are used to assess a company's profitability, solvency, and efficiency. Follow reputable financial news sources and read industry reports to stay informed about the latest trends and developments. Consider taking a course or certification in financial analysis to deepen your knowledge and skills. Remember that both technical and fundamental analysis require continuous learning and practice. The market is constantly evolving, and it's important to stay up-to-date with the latest techniques and strategies. Before making any investment decisions, conduct thorough research and consult with a qualified financial advisor. And if you're looking for a reliable broker to trade with, consider checking out XM Broker.
Combining Technical and Fundamental Analysis
The most effective approach to market analysis often involves combining technical and fundamental analysis. By integrating these two distinct perspectives, investors can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market and make more informed investment decisions. For example, a fundamental analyst might identify a company with strong financials and growth potential, while a technical analyst might use chart patterns to identify optimal entry and exit points for trading that company's stock. This hybrid approach allows investors to capitalize on both the long-term value and the short-term opportunities presented by the market. Furthermore, technical analysis can be used to confirm or challenge the findings of fundamental analysis. For example, if a company has strong financials but its stock price is trending downward, a technical analyst might identify potential reasons for the price weakness and adjust their investment strategy accordingly. Conversely, if a company has weak financials but its stock price is trending upward, a technical analyst might look for underlying technical factors that are driving the price movement. Ultimately, the goal is to use both technical and fundamental analysis to develop a holistic view of the market and make well-informed investment decisions. The key is to remain flexible and adaptable, and to continuously refine your investment strategy based on new information and changing market conditions. This ensures a well-rounded investment strategy that addresses all factors. The most successful investors are those who are able to adapt and evolve with the ever-changing market landscape.
Tips for Mastering Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Mastering technical and fundamental analysis requires a combination of education, practice, and experience. Start by building a strong foundation in the core concepts of each approach. Read books, take courses, and follow reputable financial news sources to expand your knowledge. Practice applying your knowledge by analyzing historical data and real-world market scenarios. Use charting software to identify patterns and trends, and practice calculating financial ratios and metrics. Develop a trading plan that outlines your investment goals, risk tolerance, and strategies for both technical and fundamental analysis. Stick to your plan and avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions. Continuously monitor your performance and adjust your strategies as needed. Don't be afraid to seek feedback from experienced traders and investors. Join online communities and forums to connect with like-minded individuals and learn from their experiences. Attend industry conferences and seminars to stay up-to-date with the latest trends and developments. Remember that mastering technical and fundamental analysis is a lifelong journey. The market is constantly evolving, and it's important to stay curious and keep learning. With dedication, practice, and a willingness to adapt, you can develop the skills and knowledge to become a successful investor. Use these tips to become an expert in both aspects of the market. These will help you in the long run.
The Role of Psychology in Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Psychology plays a significant role in both technical and fundamental analysis. In technical analysis, understanding investor psychology is crucial for interpreting chart patterns and identifying potential market movements. For example, a "fear of missing out" (FOMO) can drive prices higher during a bull market, while panic selling can exacerbate price declines during a bear market. Technical analysts use indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to gauge market sentiment and identify potential overbought or oversold conditions. In fundamental analysis, psychology influences investor perceptions of a company's value and growth potential. For example, positive news and analyst upgrades can boost investor confidence and drive up a company's stock price, even if the underlying fundamentals remain unchanged. Conversely, negative news and analyst downgrades can trigger a sell-off, regardless of the company's long-term prospects. Understanding the psychological biases that can influence investment decisions is essential for both technical and fundamental analysts. Confirmation bias, for example, can lead investors to selectively seek out information that confirms their existing beliefs, while ignoring contradictory evidence. Loss aversion can cause investors to hold on to losing positions for too long, hoping for a rebound. By recognizing and mitigating these biases, investors can make more rational and objective investment decisions. Market psychology can be a powerful force, influencing short-term price movements. It's important to understand its effect.
Fun Facts About Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Did you know that some technical analysts use astrological charts to predict market movements? While this approach may seem unconventional, it highlights the diversity of techniques used in technical analysis. On the other hand, Warren Buffett, one of the most successful fundamental investors of all time, famously said that he only invests in companies he understands. This underscores the importance of focusing on your circle of competence when applying fundamental analysis. Another fun fact is that the first charting software was developed in the 1960s, revolutionizing the way technical analysts visualized and interpreted market data. Today, advanced charting platforms offer a wide range of tools and indicators, making it easier than ever to analyze price patterns and trends. In the early days of fundamental analysis, investors relied on handwritten reports and snail mail to gather information about companies. Today, vast amounts of financial data are readily available online, allowing investors to conduct comprehensive research in a matter of minutes. Despite their differences, both technical and fundamental analysis have a long and fascinating history, with each approach evolving over time to adapt to changing market conditions. They both provide unique angles and methods of looking at the market. It is an ever-evolving landscape. Also, did you know that there are technical analysts who primarily trade based on news? These facts can help you better understand.
How to Choose Between Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Choosing between technical and fundamental analysis depends on your investment goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance. If you're a short-term trader looking to profit from short-term price movements, technical analysis may be a better fit. Technical analysis allows you to quickly identify patterns and trends, and to set entry and exit points based on price action and indicators. If you're a long-term investor looking to build a portfolio of fundamentally sound companies, fundamental analysis may be more appropriate. Fundamental analysis helps you identify undervalued companies with strong growth potential, and to make investment decisions based on the underlying value of the business. However, it's important to remember that neither approach is perfect. Technical analysis can generate false signals, while fundamental analysis can be slow to react to changing market conditions. The most effective approach is often to combine both technical and fundamental analysis, using each approach to complement the other. For example, you might use fundamental analysis to identify a list of potential investments, and then use technical analysis to identify optimal entry points. Alternatively, you might use technical analysis to identify a stock that is trending upward, and then use fundamental analysis to determine whether the company's financials support the price increase. Ultimately, the best approach is the one that aligns with your individual investment style and preferences. Both have their own strengths and weaknesses. Consider all factors.
What if Technical and Fundamental Analysis Disagree?
What happens when technical and fundamental analysis present conflicting signals? This is a common scenario that can leave investors feeling confused and uncertain. In such cases, it's important to carefully evaluate the underlying reasons for the disagreement and to consider the broader market context. For example, if fundamental analysis suggests that a company is undervalued, but technical analysis indicates a downtrend, it could be a sign that the market is temporarily mispricing the stock due to short-term factors. In this case, a long-term investor might choose to ignore the technical signals and focus on the company's fundamentals. On the other hand, if technical analysis suggests an uptrend, but fundamental analysis reveals significant risks or weaknesses in the company's financials, it could be a sign that the price increase is unsustainable. In this case, a short-term trader might choose to ride the momentum while carefully monitoring the underlying fundamentals. Ultimately, the decision of how to reconcile conflicting signals depends on your investment goals, time horizon, and risk tolerance. It's important to weigh the evidence from both technical and fundamental analysis, and to make a well-informed decision based on your own judgment. Also consider how the broader market is feeling and functioning. Don't panic when the signals disagree. Instead, think them through.
Listicle: 5 Key Differences Between Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Here's a quick list summarizing the key differences between technical and fundamental analysis:
- Focus: Technical analysis focuses on price charts and historical data, while fundamental analysis focuses on a company's financial statements and economic factors.
- Time Horizon: Technical analysis is often used for short-term trading, while fundamental analysis is typically used for long-term investing.
- Data Sources: Technical analysts rely on price charts, trading volume, and technical indicators, while fundamental analysts rely on financial statements, economic data, and industry reports.
- Approach: Technical analysis is based on the belief that price patterns repeat themselves over time, while fundamental analysis is based on the belief that the market will eventually recognize and correct any discrepancies between an asset's market price and its intrinsic value.
- Skills: Technical analysis requires skills in chart reading, pattern recognition, and statistical analysis, while fundamental analysis requires skills in financial accounting, economics, and industry analysis.
Understanding these differences can help you determine which approach is best suited for your investment goals and risk tolerance. Also, learn which one aligns with your preferences and resources. Take your time to see which one clicks with you. Both are very useful.
Question and Answer
Q1: What is the primary goal of technical analysis?
A1: The primary goal of technical analysis is to predict future price movements by analyzing historical price data and trading volumes.
Q2: What is the primary goal of fundamental analysis?
A2: The primary goal of fundamental analysis is to determine the intrinsic value of an asset by examining its underlying financial health and economic factors.
Q3: Can technical and fundamental analysis be used together?
A3: Yes, many investors use a combination of both technical and fundamental analysis to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the market.
Q4: Which approach is better for short-term trading?
A4: Technical analysis is generally considered to be more suitable for short-term trading, while fundamental analysis is often preferred for long-term investments.
Conclusion of The Difference Between Technical and Fundamental Analysis
Understanding the difference between technical and fundamental analysis is crucial for any investor. Whether you choose to focus on charts and patterns or delve into financial statements and economic indicators, mastering these approaches can significantly improve your investment decision-making. Remember to continuously learn, adapt, and refine your strategies to stay ahead in the ever-evolving market. And if you're looking for a platform to put your knowledge to the test, consider checking out XM for your trading needs.




0 Reviews
Your rating